SAIGE-QTL Analysis Overview
SAIGE-QTL follows a multi-step analysis pipeline designed for efficient and accurate single-cell eQTL mapping. The workflow is optimized to handle the unique challenges of single-cell data, including complex correlation structures and discrete count distributions.
Analysis Workflow
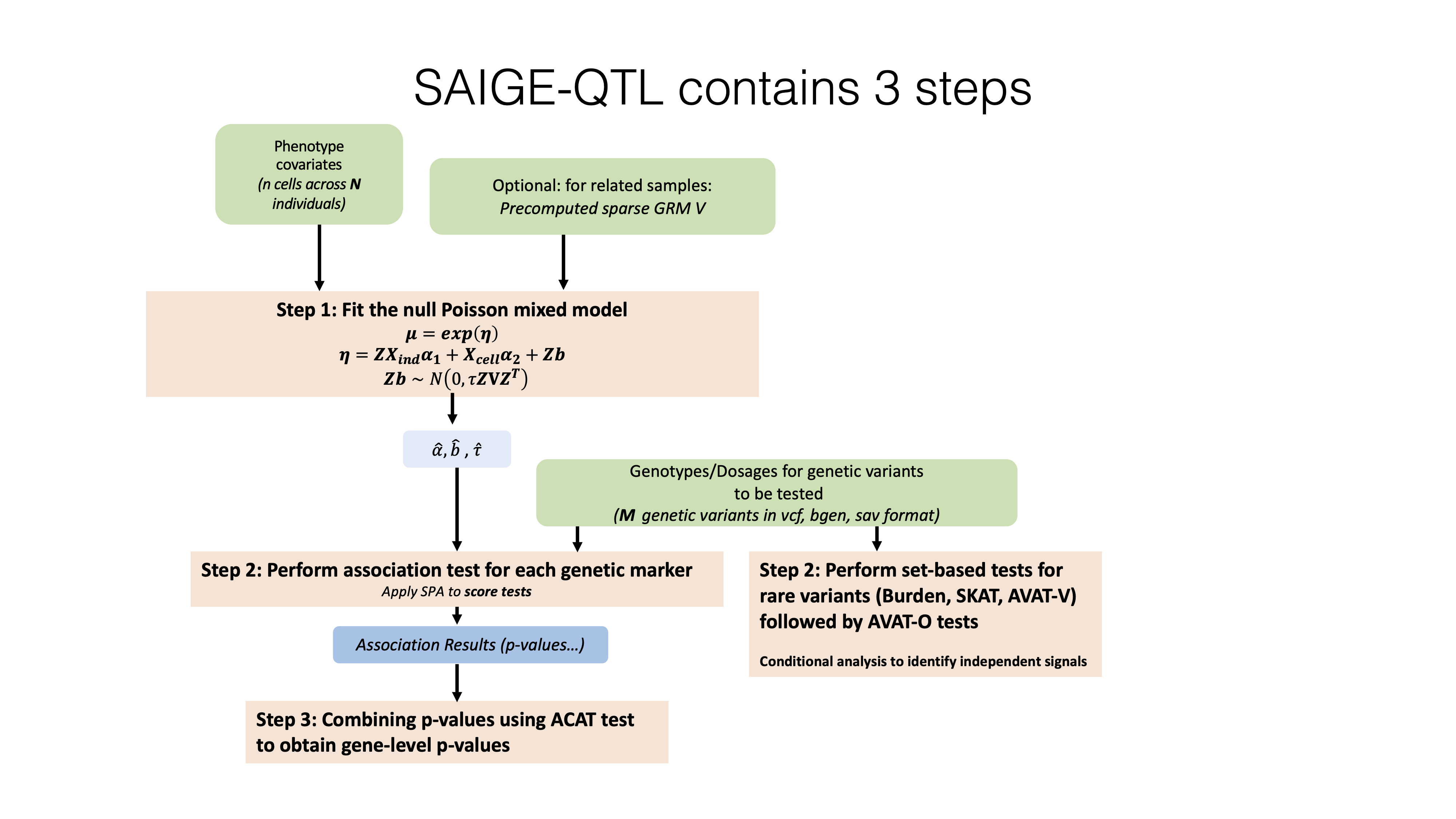
Analysis Types
SAIGE-QTL supports two main types of eQTL analysis:
1. cis-eQTL Analysis
- Tests genetic variants near genes (typically within 1Mb)
- Uses both single-variant tests (common variants) and set-based tests (rare variants)
- Steps: Step 1 → Step 2 → Step 3 (optional gene-level p-values)
2. Genome-wide eQTL Analysis
- Tests all genetic variants across the genome for each gene
- Optimized for computational efficiency when analyzing multiple genes
- Steps: Step 1 → Step 2 (batch processing multiple genes)
Key Components
Step 1: Null Model Fitting
- Fits a Poisson mixed model for each gene
- Accounts for:
- Cell-cell correlation
- Cell-level and individual-level covariates
- Total read count normalization
- Output: Model parameters and variance components for Step 2
Step 2: Association Testing
- Performs genetic association tests using the null model from Step 1
- Supports:
- Single-variant tests for common variants
- Set-based tests for rare/low-frequency variants
- Output: Association statistics and p-values
Step 3: Gene-level Analysis (Optional)
- Combines variant-level results into gene-level statistics
- Useful for rare variant analysis and pathway studies
- Output: Gene-level p-values and effect estimates
Data Requirements
Input Files
- Phenotype file: Gene expression counts with covariates
- Genotype files: PLINK, BGEN, VCF, BCF, or SAV format
- Group files: For set-based rare variant tests (optional)
Computational Considerations
Scalability Features
- Efficient memory usage for large datasets
- Parallel processing capabilities
- Optimized for:
- 20,000+ genes
- Millions of cells
- Millions of genetic variants
- Hundreds of cell types
Performance Tips
- Step 1 can be run independently for each gene (parallelizable)
- Step 2 benefits from batch processing multiple genes
- Use appropriate compute resources based on dataset size
Next Steps
- Install SAIGE-QTL - Set up your analysis environment
- Step 1 Guide - Fit null models for your genes
- Calling SAIGE-QTL - Execute the analysis pipeline
- cis-eQTL or Genome-wide eQTL - Choose your analysis type